Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Though it doesn’t cause permanent damage to the intestines, it can significantly disrupt daily life. Understanding IBS, its symptoms, root causes, and available treatment options is the first step in managing this chronic condition effectively.
What is IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)?
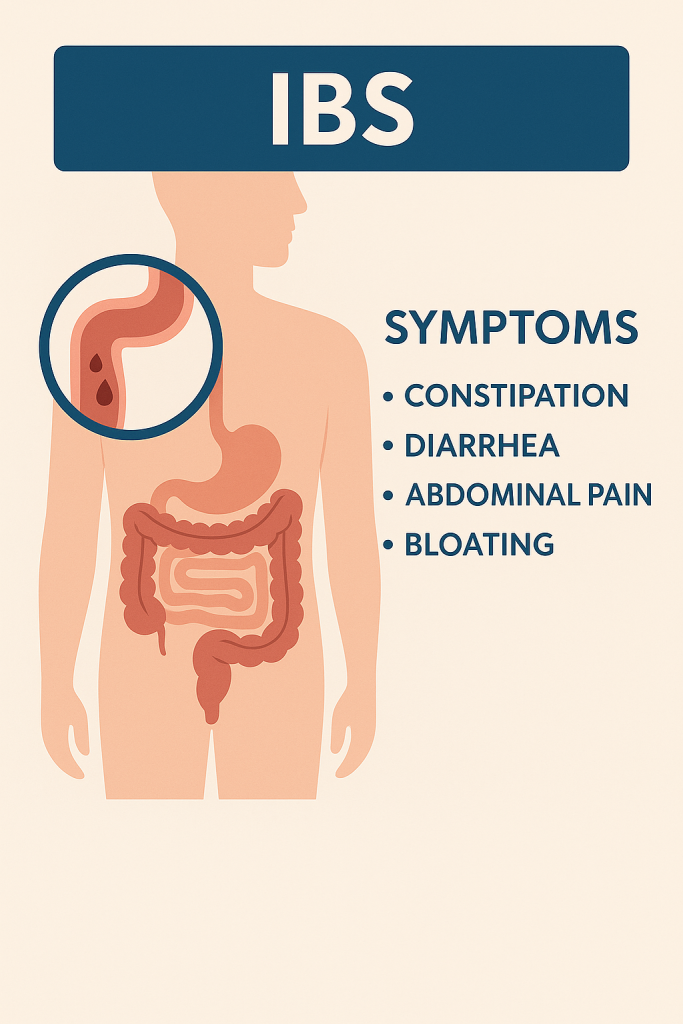
The large intestine (colon) is impacted by IBS, a functional gastrointestinal disorder. Abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and altered bowel habits like diarrhea, constipation, or both are among the symptoms that define it and usually occur together.
While IBS does not lead to serious complications or increase the risk of colorectal cancer, it can cause ongoing discomfort and a reduced quality of life for many sufferers.
Common Symptoms of IBS
How to Identify IBS Symptoms
Persistent abdominal pain is the main sign of IBS. However, each person’s presentation may differ greatly. Some people have constipation (IBS-C), diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D), or a combination of the two (IBS-M).
Frequent Symptoms Include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping (usually relieved by bowel movements)
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea or constipation, sometimes alternating between both
- Mucus in the stool
- Feeling of incomplete bowel movement
- Changes in stool consistency and frequency
These symptoms often worsen after meals or during times of stress. Symptoms must typically persist for at least 3 months to meet diagnostic criteria.
What Causes IBS?
Understanding the Root Causes of IBS
The exact cause of IBS is still unknown, but researchers believe it results from a combination of factors affecting gut-brain communication. IBS is now considered a disorder of the gut-brain axis.
Possible IBS Triggers and Risk Factors:
- Abnormal intestinal motility
- Visceral hypersensitivity – Heightened sensitivity to intestinal pain
- Intestinal inflammation
- Post-infectious IBS – Follows a bacterial or viral gastroenteritis
- Imbalance in gut microbiota
- Psychological stress – Conditions like anxiety and depression
- Hormonal influences – More common in women
Dr. Karim Shakoor, M.D., emphasizes that identifying your personal triggers through medical evaluation and dietary tracking is key to developing a successful IBS management plan.
Diagnosis of IBS
How IBS is Diagnosed by a Gastroenterologist
IBS cannot be diagnosed with a single test. Doctors use clinical assessment and rule out other conditions. Our team at Colon & Digestive Health Specialists confirms IBS using the Rome IV criteria and cutting-edge diagnostic equipment.
Criteria include:
- Recurrent abdominal pain at least one day per week in the last 3 months
- Pain associated with defecation
- Changes in bowel movement frequency and appearance
- Additional tests may be conducted to rule out inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or colorectal cancer
IBS Treatment Options
Effective Ways to Manage and Treat IBS
Although there’s no permanent cure for IBS, many treatment options are available that help manage symptoms effectively. A combination of dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, medications, and psychological therapies is often recommended.
1.Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Low FODMAP Diet:Certain fermentable carbohydrates that are known to cause IBS are eliminated by this diet. Foods are gradually reintroduced after a period of elimination in order to determine which ones trigger symptoms.
- Additional Diet Tips:
- Avoid gas-producing foods like beans and cruciferous vegetables
- Limit caffeine and alcohol
- Drink plenty of water
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
2.IBS Medications
- Depending on your IBS type, Dr. Shakoor may recommend:
- Antispasmodic drugs for cramping
- Laxatives or fiber supplements for IBS-C
- Tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs to manage pain and mental health
- Anti-diarrheal agents for IBS-D
- Antispasmodic drugs for cramping
- Laxatives or fiber supplements for IBS-C
- Anti-diarrheal agents for IBS-D
3.Tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs to manage pain and mental health
Psychological approaches such as Cognitive Probiotics may help balance the gut microbiome. Dr. Shakoor often recommends specific strains based on individual needs. Therapy (CBT) and gut-directed hypnotherapy are highly effective for stress-related IBS.
4. Probiotics and Gut Health
Probiotics may help balance the gut microbiome. Dr. Shakoor often recommends specific strains based on individual needs.
Long-Term IBS Management
Living Better with IBS
Despite being chronic, IBS is manageable. Numerous patients treated by Dr. Karim Shakoor, M.D., report notable improvements in their quality of life and symptoms.
Self-care and Management Tips:
- Keep a symptom and food journal
- Follow a personalized IBS diet
- Practice stress-reduction techniques
- Stay active and hydrated
Symptoms That Need Immediate Medical Attention
IBS symptoms can mimic those of more serious conditions. Seek medical attention if you notice:
- Blood in the stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue or anemia
- Severe or worsening abdominal pain
- Family history of colon cancer
Conclusion
Understanding IBS is key to managing it effectively. Whether you’re struggling with bloating, pain, constipation, or diarrhea, Dr. Karim Shakoor, M.D. at Colon & Digestive Health Specialists can provide expert care and compassionate support.
Book your appointment today at Colon & Digestive Health Specialists and take the first step toward better digestive health.
